Background: Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) was characterized as ineffective hematopoiesis, increased transformation to acute myeloid leukemia (AML), and accompanied by immune system dysfunction. However, the immune signature of MDS remains elusive.
Methods: The clinical data (age, sex, international prognostic score system (IPSS), hemoglobin, blast, RBC transfusion dependence, and corresponding subject-level survival) as well as expression profiles of MDS (CD34+ cells) were obtained from Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO: GSE 58831; GSE 114922). A robust prognosis model of immune genes was constructed by the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression analysis. Survival analysis for prognostic model was carried out through the Kaplan‐Meier curve and Log‐rank test. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves and area under the curve (AUC) were used to assess the accuracy of prognostic models. Immune score for different subtype were calculated further by single sample gene set enrichment analysis (ssGSEA).
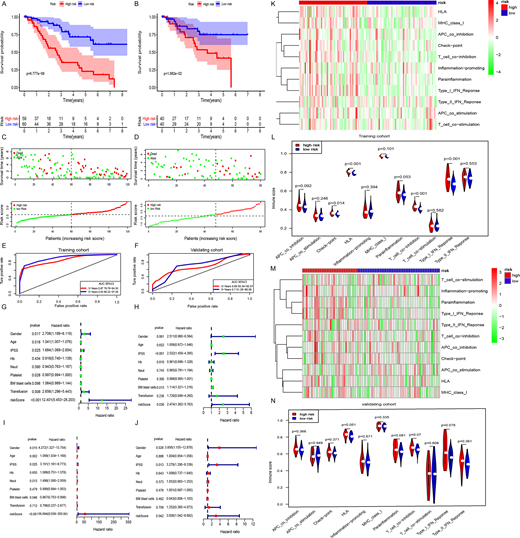
Result: A novel robust immune gene prognostic model indicate that subtype with lower risk score were longer overall survival (OS) than subtype with higher risk score in training cohort (Figure1 A, C). The model was further verified by the validation cohort (Figure1 B, D). The multivariate Cox regression analysis demonstrated the model was an independent prognostic factor for OS prediction with hazard ratios of 56.694 (95% CIs: 9.038−355.648), 3.009 (95% CIs: 1.042−8.692) both in train cohort and external validation cohort respectively (Figure1 G, H). The AUC of 5- year were 0.92 (95% CIs: 0.86 - 0.97) and 0.7 (95% CIs: 0.51 - 0.89) for OS respectively in training cohort and validation cohort (Figure1 E, F). Furthermore, ssGSEA showed higher risk score subtype was significantly associated with higher immune score of check point, human leukocyte antigen (HLA), T cell co-inhibition and type I interferon (IFN) response (Figure1 K-N), which indicating that the poor outcome might be caused by tumor-associated immune response dysfunction partly.
Conclusion: We constructed a robust immune gene prognostic model, which have a potential prognostic value for MDS patients and may provide evidence for personalized immunotherapy.
No relevant conflicts of interest to declare.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal